ketoacidosis is most commonly found in type 2 diabetes Ketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology dehydration acidosis hyperglycemia mellitus hypoglycemia diabetestalk metabolic disambiguation hyperglycemic hyperosmolar
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be categorized into different types, including type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In addition to these types, another serious complication that can arise in diabetic individuals is called diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). This condition occurs when there is a severe lack of insulin in the body, resulting in high levels of blood sugar (glucose) and the production of ketones.
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and Type 2:
Diabetes mellitus type 1 is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This leads to an absolute deficiency of insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood glucose levels.
On the other hand, diabetes mellitus type 2 is a metabolic disorder that is often associated with insulin resistance. In this condition, the body still produces insulin, but it becomes less effective at controlling blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes is often linked to lifestyle factors such as excessive weight, physical inactivity, and poor dietary choices.
In both types of diabetes, elevated blood glucose levels can have detrimental effects on various organs and systems in the body, including the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and cardiovascular system.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA):
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a life-threatening complication that can occur in individuals with type 1 diabetes, although it can also rarely affect individuals with type 2 diabetes. DKA arises when there is a scarcity of insulin in the body, leading to an imbalance in blood sugar levels and the production of ketones.
Ketones are by-products of fat breakdown that accumulate in the blood when the cells cannot utilize glucose for energy due to the lack of insulin. High levels of ketones can change the pH balance of the blood, making it acidic. This acidosis can lead to electrolyte imbalances and severe complications such as coma or even death.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of DKA:
It is crucial for individuals with diabetes and their healthcare providers to be aware of the warning signs and symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis. Prompt recognition and treatment can help prevent further complications.
Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Excessive thirst and frequent urination
- Abdominal pain and discomfort
- Nausea and vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Confusion and fatigue
If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately, as diabetic ketoacidosis requires urgent evaluation and treatment in a hospital setting.
Prevention and Management:
Preventing diabetic ketoacidosis starts with managing diabetes effectively. For individuals with type 1 diabetes, this involves consistent insulin administration and monitoring blood sugar levels. It is crucial to work closely with healthcare providers to establish an insulin regimen tailored to individual needs.
For those with type 2 diabetes, lifestyle modifications play a key role in managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis. Healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and weight management are integral components of diabetes management.
In conclusion, diabetes mellitus and diabetic ketoacidosis are serious conditions that require diligent management and healthcare supervision. Understanding the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, as well as recognizing the signs and symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis, can empower individuals and their healthcare providers to take proactive measures to prevent and manage these conditions effectively.
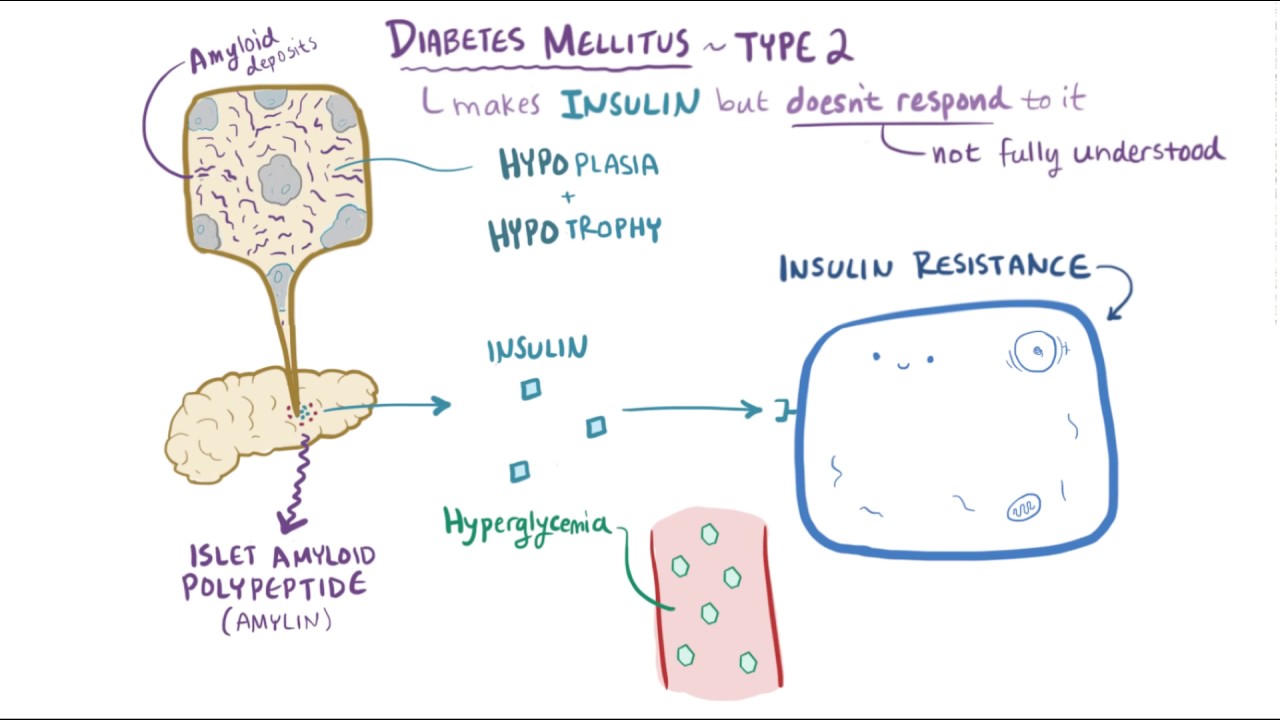 Diabetes mellitus type 1, type 2 & diabetic ketoacidosis DKA causes
Diabetes mellitus type 1, type 2 & diabetic ketoacidosis DKA causes
Image Source: https://i.ytimg.com/vi/3eSWGp1Ulpw/maxresdefault.jpg
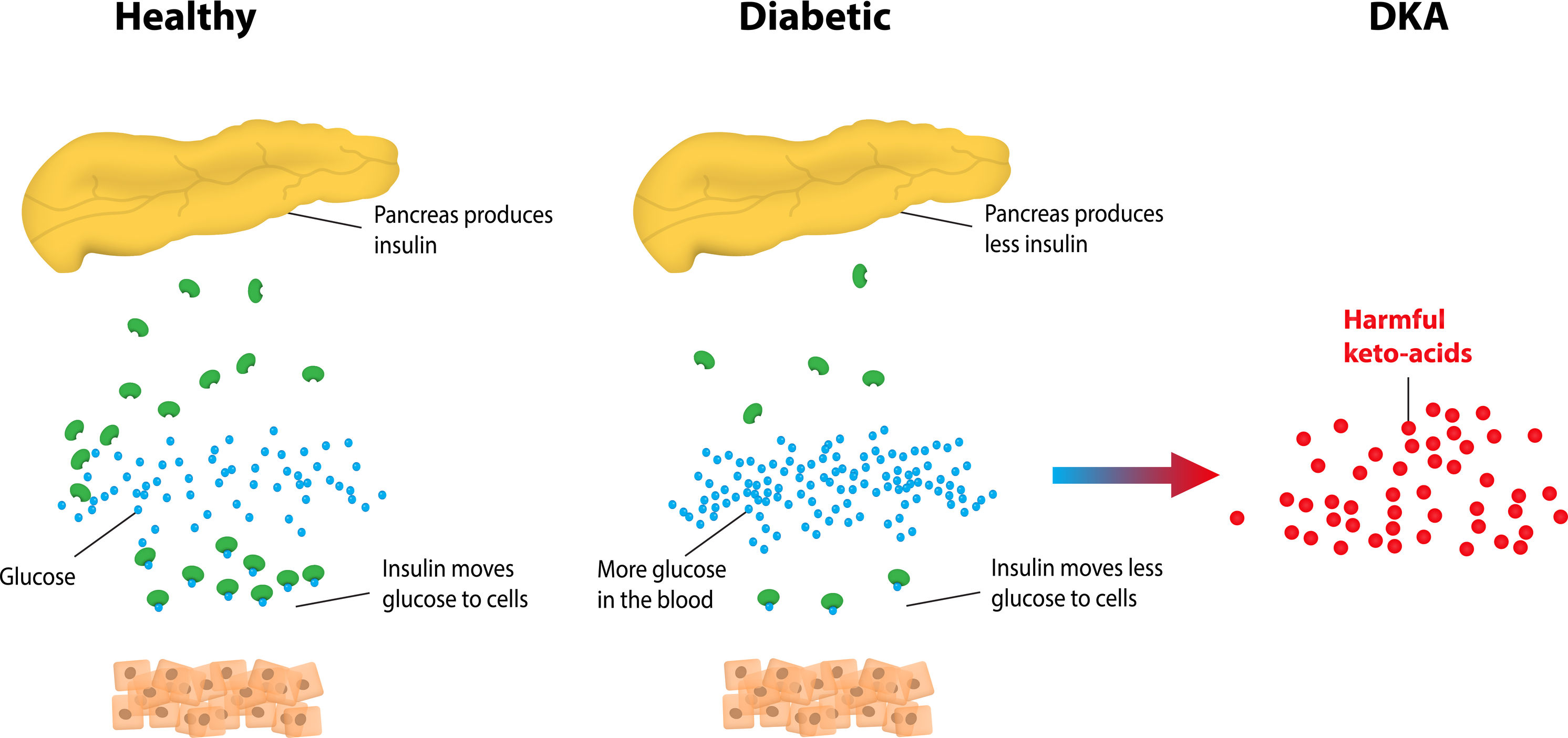 Ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis
Image Source: http://diseasesandconditions.net/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2015/06/35088040_l.jpg
If you are looking for Diabetes mellitus type 1, type 2 & diabetic ketoacidosis DKA causes you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pictures about Diabetes mellitus type 1, type 2 & diabetic ketoacidosis DKA causes like Pin on DIABETIC FOOD/INFO, Why Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cause Dehydration — DiabetesCareTalk.net and also diabetic ketoacidosis | diabetic food,drink,desert and things you nee…. Read more:
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1, Type 2 & Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA Causes
 www.youtube.comdiabetes type ketoacidosis dka diabetic causes mellitus symptoms
www.youtube.comdiabetes type ketoacidosis dka diabetic causes mellitus symptoms
Ketoacidosis
 diseasesandconditions.netketoacidosis diabetes dka diabetic type ketones understanding blood definition symptoms pathophysiology ketogenic diet complications ketosis keytones live fever risks sugar
diseasesandconditions.netketoacidosis diabetes dka diabetic type ketones understanding blood definition symptoms pathophysiology ketogenic diet complications ketosis keytones live fever risks sugar
Why Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cause Dehydration — DiabetesCareTalk.net
 www.diabetescaretalk.netketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology dehydration acidosis hyperglycemia mellitus hypoglycemia diabetestalk metabolic disambiguation hyperglycemic hyperosmolar
www.diabetescaretalk.netketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology dehydration acidosis hyperglycemia mellitus hypoglycemia diabetestalk metabolic disambiguation hyperglycemic hyperosmolar
Diabetic Ketoacidosis | Diabetic Food,drink,desert And Things You Nee…
 pinterest.comketoacidosis diabetic mechanism mathematician biologist sigh
pinterest.comketoacidosis diabetic mechanism mathematician biologist sigh
Pin On DIABETIC FOOD/INFO
 www.pinterest.comdiabetic ketoacidosis prevention fruity odor a1c symptoms pain icu
www.pinterest.comdiabetic ketoacidosis prevention fruity odor a1c symptoms pain icu
Pin on diabetic food/info. Ketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology dehydration acidosis hyperglycemia mellitus hypoglycemia diabetestalk metabolic disambiguation hyperglycemic hyperosmolar. Why does diabetic ketoacidosis cause dehydration — diabetescaretalk.net